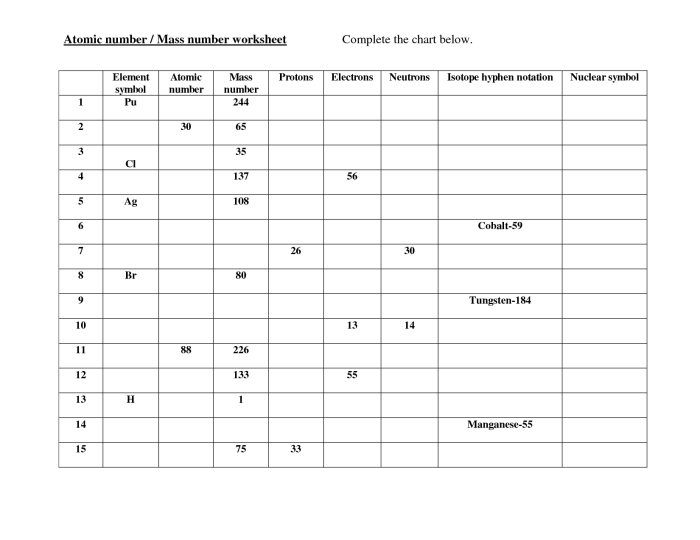
Chemistry worksheet atomic number and mass number – Delve into the fascinating world of chemistry with our comprehensive worksheet on atomic number and mass number. This in-depth resource provides a clear understanding of these fundamental concepts, empowering you to unravel the intricacies of the elements that shape our universe.
Through engaging examples and insightful explanations, we embark on a journey to explore the significance of atomic and mass numbers in identifying, classifying, and understanding the behavior of elements.
Atomic Number: Chemistry Worksheet Atomic Number And Mass Number
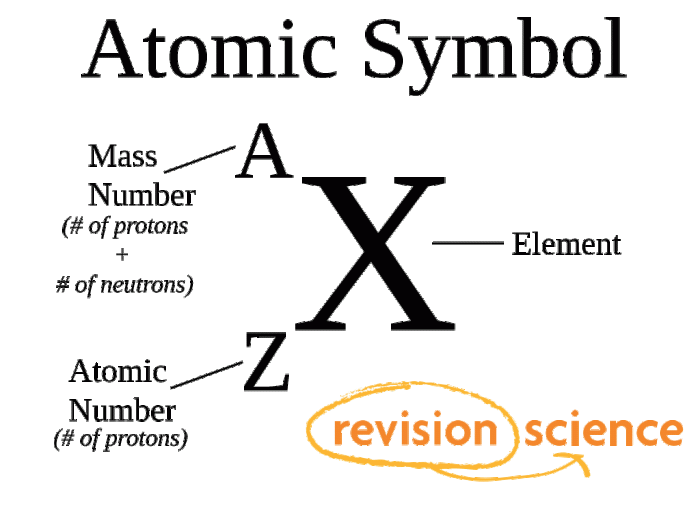
The atomic number of an element is the number of protons in its nucleus. Each element has a unique atomic number that distinguishes it from all other elements. For example, hydrogen has an atomic number of 1, helium has an atomic number of 2, and oxygen has an atomic number of 8.
The atomic number of an element is significant because it determines the element’s chemical properties. Elements with the same atomic number have the same number of electrons, which in turn determines their chemical behavior.
Mass Number, Chemistry worksheet atomic number and mass number
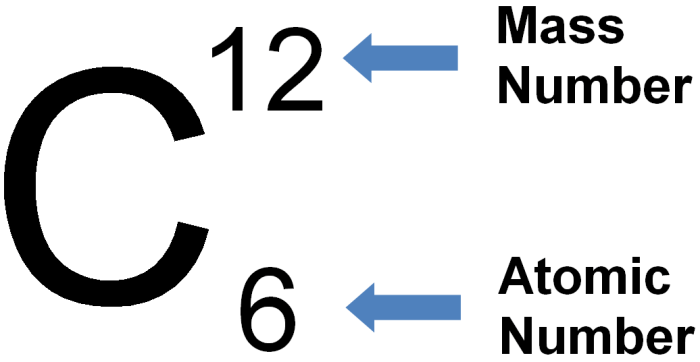
The mass number of an element is the total number of protons and neutrons in its nucleus. The mass number is typically represented by the symbol A. For example, the mass number of carbon-12 is 12, which means that it has 6 protons and 6 neutrons in its nucleus.
The mass number of an element is important because it determines the element’s atomic mass. The atomic mass of an element is the weighted average of the masses of all of its isotopes. For example, the atomic mass of carbon is 12.011, which means that it is an average of the masses of carbon-12, carbon-13, and carbon-14.
Isotopes
Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have the same atomic number but different mass numbers. This means that isotopes have the same number of protons and electrons, but different numbers of neutrons. For example, carbon-12, carbon-13, and carbon-14 are all isotopes of carbon.
They all have 6 protons and 6 electrons, but they have different numbers of neutrons (6, 7, and 8, respectively).
Isotopes are used in a variety of applications, including:
- Radioactive isotopes are used in medicine to diagnose and treat diseases.
- Stable isotopes are used in geochemistry to study the history of the Earth.
- Isotopes are also used in nuclear power plants to generate electricity.
Periodic Table
The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of the chemical elements, organized by their atomic number, electron configuration, and recurring chemical properties. The periodic table is used to predict the properties of elements and to understand their chemical behavior.
The periodic table is organized into 18 vertical columns, called groups, and 7 horizontal rows, called periods. The groups are numbered 1-18 from left to right, and the periods are numbered 1-7 from top to bottom.
Elements in the same group have similar chemical properties. For example, all of the alkali metals (Group 1) are highly reactive and form 1+ ions. All of the halogens (Group 17) are highly reactive and form 1- ions.
Elements in the same period have the same number of electron shells. For example, all of the elements in the second period have two electron shells.
Applications of Atomic and Mass Numbers
Atomic and mass numbers are used in a variety of applications in chemistry, including:
- Determining the elemental composition of a compound.
- Predicting the properties of an element.
- Understanding the structure of atoms.
Atomic and mass numbers are also used in nuclear physics to study the structure of the nucleus and the interactions between nucleons.
Questions and Answers
What is the difference between atomic number and mass number?
Atomic number represents the number of protons in an atom’s nucleus, defining its elemental identity. Mass number, on the other hand, is the sum of protons and neutrons in the nucleus, indicating the total mass of the atom.
How are isotopes related to atomic and mass numbers?
Isotopes are atoms of the same element with identical atomic numbers but different mass numbers. This variation arises from differences in the number of neutrons in their nuclei.
What is the significance of the periodic table in understanding atomic and mass numbers?
The periodic table organizes elements based on their atomic numbers, revealing periodic trends in their properties. By examining an element’s position in the table, we can infer its atomic and mass numbers, as well as predict its chemical behavior.