Draw an alternative lewis structure for the incomplete structure – In chemistry, the concept of alternative Lewis structures plays a crucial role in understanding the electronic structure and bonding behavior of molecules. This article delves into the concept of alternative Lewis structures, their significance in completing incomplete Lewis structures, and their applications in predicting molecular properties.
Lewis structures, also known as electron-dot structures, are a powerful tool for representing the distribution of electrons in molecules. However, in certain cases, a single Lewis structure may not fully capture the electronic delocalization within a molecule. This is where the concept of alternative Lewis structures comes into play.
Alternative Lewis Structure
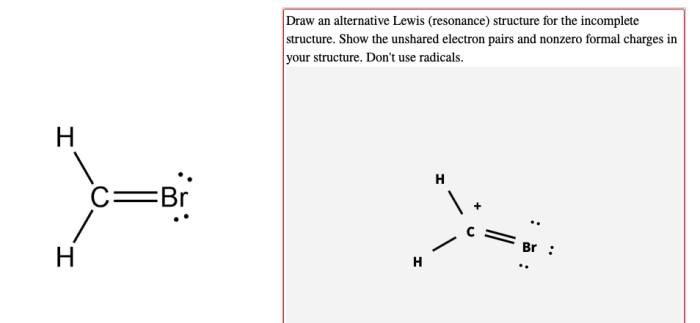
Lewis structures are commonly used to represent the bonding and arrangement of atoms in a molecule. However, for some molecules, a single Lewis structure cannot fully describe their electronic structure. In such cases, alternative Lewis structures are used to represent the resonance hybrid of the molecule.
Resonance is a phenomenon that occurs when a molecule can exist in two or more Lewis structures that have the same arrangement of atoms but differ in the distribution of electrons. The resonance structures are interconverted by the movement of electrons, and the actual structure of the molecule is a hybrid of all the resonance structures.
Significance of Resonance, Draw an alternative lewis structure for the incomplete structure
Resonance is a fundamental concept in chemistry that has important implications for understanding the bonding and properties of molecules. It helps explain the stability and reactivity of molecules, and it can be used to predict the outcomes of chemical reactions.
Examples of Molecules with Alternative Lewis Structures
Many molecules exhibit resonance, including:
- Benzene
- Carbon dioxide
- Ozone
- Nitrobenzene
- Pyridine
Incomplete Lewis Structure
An incomplete Lewis structure is a Lewis structure that does not show all of the lone pairs of electrons on the atoms. Incomplete Lewis structures are often used as a starting point for drawing resonance structures.
Steps Involved in Completing a Lewis Structure
- Draw the skeletal structure of the molecule.
- Add electrons to the atoms to satisfy the octet rule.
- If there are any remaining electrons, place them in lone pairs on the atoms.
Role of Resonance in Completing Lewis Structures
Resonance can play a role in completing Lewis structures. In some cases, a molecule may have multiple resonance structures, and the incomplete Lewis structure may not show all of the resonance structures. In such cases, it is necessary to draw all of the resonance structures in order to complete the Lewis structure.
Drawing Alternative Lewis Structures
To draw alternative Lewis structures, follow these steps:
- Draw the incomplete Lewis structure of the molecule.
- Identify the atoms that can have multiple bonds.
- Move electrons to form multiple bonds between the atoms.
- Draw the resonance structures that result from the movement of electrons.
Importance of Considering Resonance
It is important to consider resonance when drawing alternative Lewis structures because resonance can affect the stability and reactivity of the molecule. The resonance structures that are drawn should be the most stable resonance structures.
Examples
Consider the molecule ozone (O3). The incomplete Lewis structure of ozone is:
O=O-O
There are two possible resonance structures for ozone:
O-O=OO–-O +=O
The second resonance structure is more stable than the first resonance structure because it has a lower formal charge.
Resonance Structures
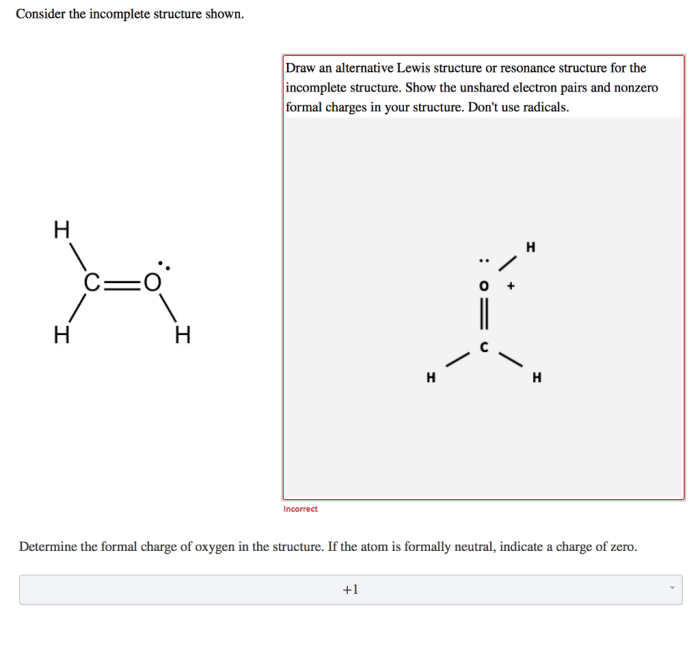
Resonance structures are two or more Lewis structures that have the same arrangement of atoms but differ in the distribution of electrons. Resonance structures are interconverted by the movement of electrons, and the actual structure of the molecule is a hybrid of all the resonance structures.
Criteria for Drawing Resonance Structures
- The resonance structures must have the same number of valence electrons.
- The resonance structures must have the same arrangement of atoms.
- The resonance structures must have the same formal charges on each atom.
Comparison of Resonance Structures with Lewis Structures
| Property | Lewis Structure | Resonance Structure |
|---|---|---|
| Number of valence electrons | Equal to the number of valence electrons in the molecule | Equal to the number of valence electrons in the molecule |
| Arrangement of atoms | Shows the arrangement of atoms in the molecule | Shows the arrangement of atoms in the molecule |
| Distribution of electrons | Shows the distribution of electrons in the molecule | Shows one possible distribution of electrons in the molecule |
| Formal charges | Shows the formal charges on each atom | Shows the formal charges on each atom |
Applications of Alternative Lewis Structures
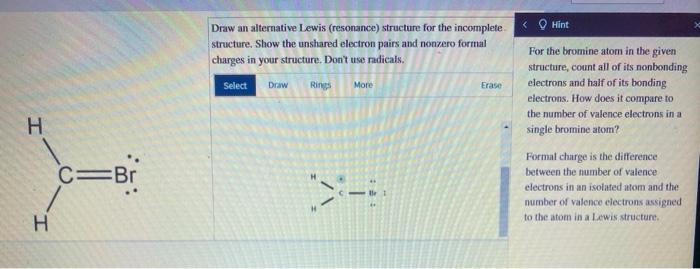
Alternative Lewis structures have a number of applications in chemistry, including:
- Predicting the stability and reactivity of molecules
- Explaining the mechanisms of chemical reactions
- Designing new molecules with desired properties
Predicting Molecular Properties
Alternative Lewis structures can be used to predict the stability and reactivity of molecules. The most stable resonance structure is the one with the lowest energy. The energy of a resonance structure can be calculated using quantum mechanics.
Explaining the Mechanisms of Chemical Reactions
Alternative Lewis structures can be used to explain the mechanisms of chemical reactions. The transition state of a chemical reaction is a high-energy intermediate that is formed during the reaction. The transition state can be represented by a resonance structure.
Designing New Molecules
Alternative Lewis structures can be used to design new molecules with desired properties. For example, a molecule with a particular functional group can be designed by choosing the appropriate resonance structure.
Detailed FAQs: Draw An Alternative Lewis Structure For The Incomplete Structure
What is the purpose of drawing alternative Lewis structures?
Alternative Lewis structures provide a more accurate representation of the electronic delocalization within a molecule, which can help predict molecular properties and reactivity.
How do I know when a molecule has alternative Lewis structures?
Molecules with resonance structures typically have multiple equivalent Lewis structures that can be drawn by moving electrons around without changing the overall connectivity of the atoms.
What are the limitations of Lewis structures?
Lewis structures do not provide information about the three-dimensional shape of a molecule or the energy levels of its electrons.