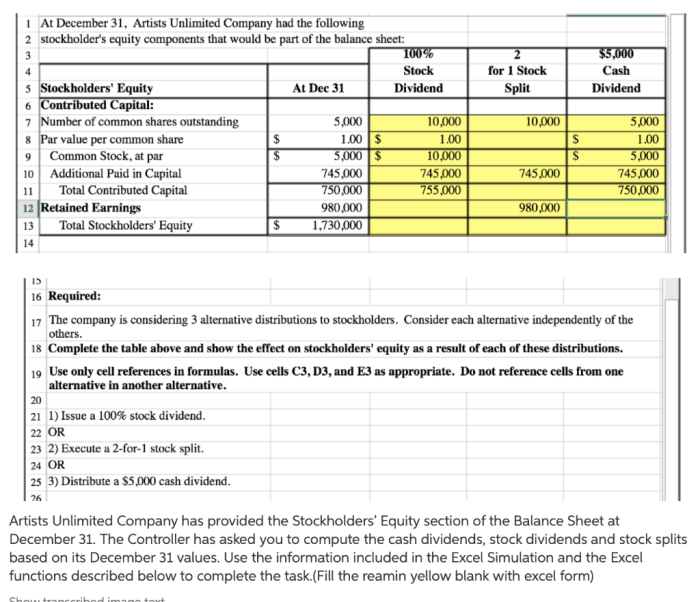
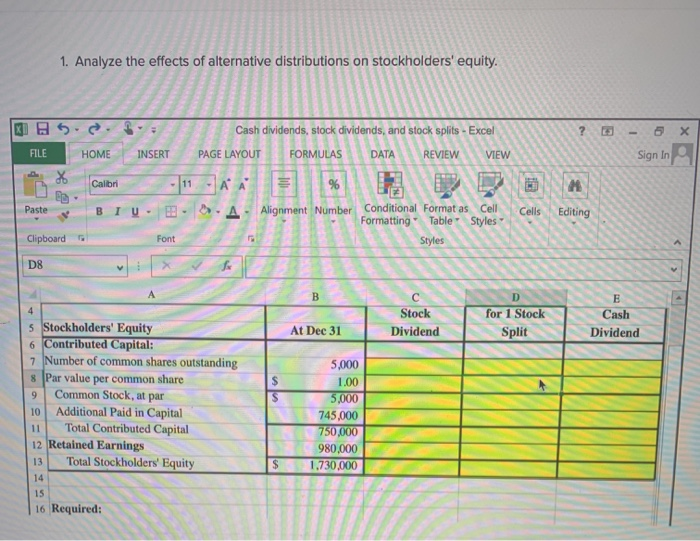
Analyze the effects of alternative distributions on stockholders’ equity – This comprehensive analysis delves into the intricate relationship between alternative distributions and stockholders’ equity, unraveling their impact on financial statements, tax implications, and strategic decision-making for corporations.
Alternative distributions, encompassing stock dividends, stock splits, and spin-offs, offer corporations a multifaceted tool to manage their capital structure and engage with shareholders. By examining the accounting treatment, financial effects, and tax consequences of these distributions, we gain a deeper understanding of their implications for both the issuing company and its stakeholders.
Definition and Types of Alternative Distributions: Analyze The Effects Of Alternative Distributions On Stockholders’ Equity
Alternative distributions are non-cash distributions made by a corporation to its shareholders instead of dividends. These distributions can impact stockholders’ equity, which represents the residual interest in the assets of the corporation after deducting liabilities.
Common Types of Alternative Distributions
- Stock dividends: Distributions of additional shares of the issuing corporation’s common stock to existing shareholders.
- Stock splits: Divisions of existing shares into a larger number of shares, increasing the number of shares outstanding.
- Spin-offs: Distributions of shares in a new or existing subsidiary corporation to existing shareholders.
Accounting Treatment of Alternative Distributions

Alternative distributions are recorded based on their fair market value at the date of distribution. The book value of the shares distributed is transferred from retained earnings to share capital.
Effects on Financial Statements
- Balance sheet: Increases share capital and reduces retained earnings.
- Income statement: No direct impact on income or expenses.
Impact on Stockholders’ Equity
Alternative distributions generally have a neutral impact on total stockholders’ equity, as they redistribute existing equity among shareholders.
Positive Impacts
- Increased liquidity: Stock dividends and splits increase the number of shares outstanding, potentially increasing liquidity.
- Enhanced shareholder value: Spin-offs can create separate entities with distinct market valuations, potentially enhancing overall shareholder value.
Negative Impacts
- Reduced book value per share: Stock dividends and splits reduce the book value per share, potentially impacting dividend payouts and earnings per share.
- Transaction costs: Spin-offs can involve significant transaction costs, which can impact stockholders’ equity.
Tax Implications of Alternative Distributions
Alternative distributions can have tax consequences for both the corporation and the shareholders.
Corporate Taxation
- Stock dividends: Generally not taxable to the corporation.
- Stock splits: Not taxable to the corporation.
- Spin-offs: May trigger capital gains tax if the distribution is not tax-free.
Shareholder Taxation
- Stock dividends: Generally not taxable to shareholders if the distribution is less than 25% of the shares outstanding.
- Stock splits: Not taxable to shareholders.
- Spin-offs: May be taxable as capital gains or dividends, depending on the circumstances.
Strategic Considerations for Corporations
Corporations may issue alternative distributions for various strategic reasons.
Benefits, Analyze the effects of alternative distributions on stockholders’ equity
- Tax optimization: Spin-offs can be used to separate taxable and non-taxable entities.
- Increased liquidity: Stock dividends and splits can enhance share liquidity, attracting investors.
- Enhanced shareholder engagement: Spin-offs can create separate companies with distinct growth prospects, potentially increasing shareholder engagement.
Risks
- Reduced control: Spin-offs can result in the corporation losing control of the distributed entity.
- Transaction costs: Alternative distributions can involve significant transaction costs.
- Negative market reaction: Spin-offs can sometimes lead to negative market reactions if investors perceive the distribution as unfavorable.
Case Studies and Examples
Example 1: Apple Inc.In 2020, Apple Inc. issued a 4-for-1 stock split. The stock split increased the number of shares outstanding from 2.2 billion to 8.8 billion. The book value per share decreased from $53.54 to $13.39, but the total stockholders’ equity remained unchanged.
Example 2: General Electric Co.In 2019, General Electric Co. completed a spin-off of its healthcare business, creating a separate publicly traded company called GE Healthcare Technologies Inc. The spin-off was intended to enhance the focus and growth potential of both entities.
Common Queries
What are the primary types of alternative distributions?
Common types include stock dividends, stock splits, and spin-offs.
How do alternative distributions affect the balance sheet?
They typically reduce retained earnings and may impact share capital and other equity accounts.
What are the tax implications of alternative distributions for shareholders?
Tax treatment varies depending on the type of distribution and the individual’s tax situation.
